Server virtualization in cloud computing has changed the way businesses operate by making computing resources more flexible and efficient. It allows a single physical server to act as multiple virtual servers, improving performance, reducing costs, and enhancing scalability. The adoption of server virtualization in cloud computing has increased dramatically, making it a core component of modern IT infrastructure.
One of the key players in this field is Viria, a leader in virtualization technology that helps businesses optimize their IT infrastructure. As the demand for virtualized environments grows, understanding how server virtualization in cloud computing works and its advantages is crucial.
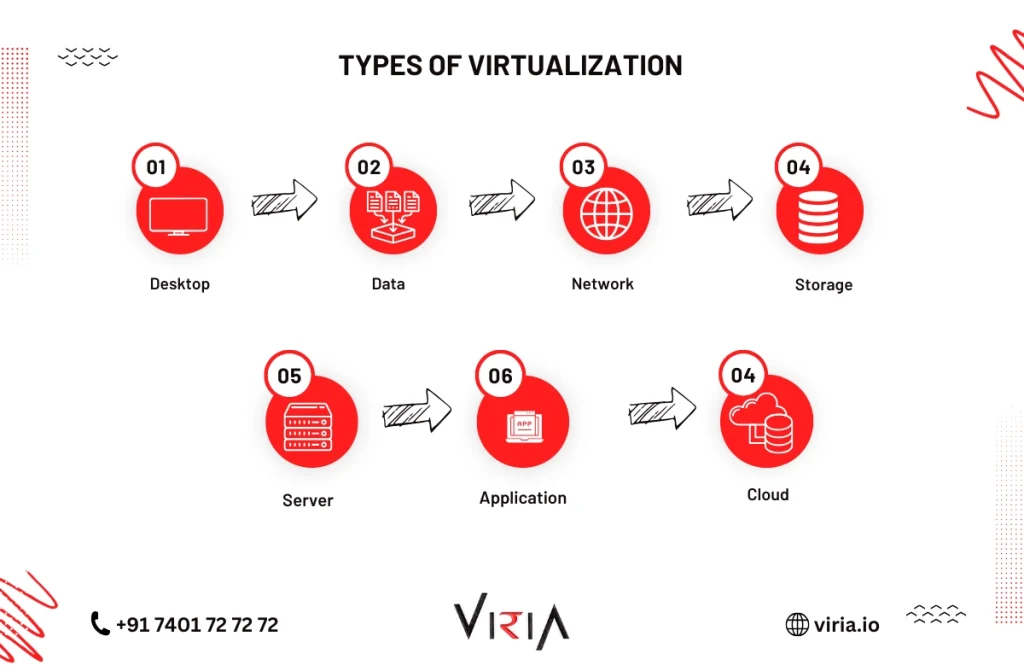
What is Virtual Server in Cloud Computing?
What is virtual server in cloud computing? It is a software-based server that operates within a physical server. Instead of dedicating an entire machine to a single task, virtualization allows multiple virtual servers to share resources while running independently. This method enhances efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in cloud environments.
Features of Virtual Servers
- Resource Efficiency: Virtual servers optimize CPU, memory, and storage usage by distributing them across multiple virtual machines.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily scale their virtual servers up or down based on demand without requiring additional hardware.
- Cost Savings: Reducing the need for physical hardware lowers maintenance and energy costs.
How Does a Virtual Server Work?
What is virtual server in cloud computing? It functions using a hypervisor, a special software layer that enables virtualization. The hypervisor divides the physical server into multiple isolated virtual servers, ensuring independent operation and resource optimization.
Steps of Virtual Server Operation:
- Hardware Allocation: The hypervisor assigns specific CPU, RAM, and storage to each virtual server.
- Software Layering: Each virtual server runs its own operating system and applications independently.
- Resource Sharing: Multiple virtual servers share the same physical resources but remain isolated from one another.
This method ensures better utilization of computing resources while maintaining security and efficiency, making server virtualization in cloud computing highly beneficial.
Why Choose Virtual Servers?
Many businesses ask, “What is virtual server in cloud computing?” and why it is essential. Virtual servers provide flexibility, cost savings, and optimal performance without requiring heavy investments in hardware. They allow seamless cloud integration and ensure better management of IT resources.
Benefits of Virtual Servers
Server virtualization in cloud computing provides numerous advantages for businesses and organizations.
- Improved Performance: Virtualization maximizes resource usage, leading to faster processing and better efficiency.
- Lower Costs: Businesses save money on hardware, maintenance, and energy consumption.
- Greater Flexibility: Virtual servers can be moved or modified quickly based on organizational needs.
- Disaster Recovery: Virtualization allows quick backups and recovery, reducing downtime during failures.
Virtual Server Challenges
Despite its many benefits, virtual server in cloud computing comes with some challenges.
- Security Risks: If not managed properly, virtual environments can be vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Resource Overhead: Running multiple virtual server in cloud computing on a single machine can strain resources if not optimized correctly.
- Complex Management: Managing multiple virtual machines requires specialized knowledge and tools.
Organizations must address these challenges to fully leverage the benefits of server virtualization in cloud computing.
Virtual Private Servers and Web Hosting
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a type of virtual server commonly used in web hosting. A VPS provides users with a dedicated portion of a physical server while keeping their data isolated from others. Server virtualization in cloud computing makes VPS hosting possible by partitioning a physical server into multiple virtual environments.
Advantages of VPS for Web Hosting:
- Better Performance: Unlike shared hosting, VPS users get dedicated resources, ensuring faster website performance.
- Enhanced Security: Data isolation prevents breaches from other users on the same server.
- Customization: Users have full control over their VPS environment, allowing them to install custom software.
With server virtualization in cloud computing, businesses benefit from cost-effective and scalable hosting solutions. This technology optimizes server usage while ensuring security and performance.
Server Virtualization in Cloud Computing is a technology that enables multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server. This process improves resource utilization, reduces operational costs, and enhances scalability. Organizations benefit from server virtualization as it allows efficient management of computing resources without the need for extensive hardware investments.
What is Server Virtualization in Cloud Computing?
Server virtualization in cloud computing is the process of partitioning a physical server into multiple isolated virtual servers using a hypervisor. These virtual machines (VMs) operate independently, allowing users to deploy various applications and services on a single physical infrastructure. This technology ensures better resource allocation and optimizes performance for cloud-based environments.
Benefits of Server Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces hardware expenses by consolidating multiple virtual servers onto fewer physical machines.
- Scalability: Easily scales resources up or down based on demand without requiring additional hardware.
- Improved Resource Utilization: Maximizes CPU, memory, and storage usage by distributing workloads efficiently.
- Disaster Recovery: Enhances data backup and recovery processes with snapshot and failover capabilities.
- Enhanced Security: Isolates virtual machines, preventing security threats from affecting the entire system.
Virtual Servers Versus Virtual Machines
Many people confuse virtual servers with virtual machines, but they have distinct differences.
- Virtual Machines (VMs): Each VM operates as a complete computer system with its own operating system and software.
- Virtual Servers: These are specific virtualized server environments running within a single physical server.
Server virtualization in cloud computing optimizes virtual servers for hosting websites, applications, and databases, while VMs can be used for a variety of purposes, including running different operating systems on the same hardware.
What is a Virtual Desktop?
A virtual desktop is a cloud-based system that allows users to access a full desktop environment remotely. Instead of running an operating system on a physical computer, a virtual desktop delivers it over the internet.
Benefits of Virtual Desktops:
- Remote Access: Users can access their desktops from any device, anywhere.
- Improved Security: Centralized storage reduces the risk of data loss or theft.
- Cost-Effective: Businesses save money on physical computer maintenance and upgrades.
Why Server Virtualization?
Server virtualization in cloud computing is essential for organizations looking to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Maximizes Hardware Usage: Virtualization ensures servers run at full capacity rather than leaving resources idle.
- Simplifies Management: IT teams can manage multiple virtual servers from a single interface.
- Enhances Disaster Recovery: Virtualization allows quick recovery of systems in case of failure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Server Virtualization
Advantages:
- Cost Savings: Less hardware means lower capital and operational costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Virtualized servers consume less power compared to multiple physical servers.
- Faster Deployment: IT teams can quickly create and deploy new servers.
Disadvantages:
- Performance Issues: Poorly configured virtual servers can lead to slow processing speeds.
- Security Risks: Virtual environments can be targeted by cyber-attacks if not properly secured.
- Complexity: Managing a virtualized environment requires specialized knowledge.
How is Server Virtualization Used?
Server virtualization in cloud computing is used across various industries for different purposes.
- Cloud Computing: Major cloud providers use virtualization to deliver flexible computing resources.
- Enterprise IT: Businesses use virtualization for cost-effective IT management.
- Disaster Recovery: Virtualization enables quick backups and system restorations.
HPE and Virtual Servers
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) is a leader in virtualization technology.
HPE’s Virtualization Solutions:
- HPE ProLiant Servers: These servers are optimized for virtualization, offering high performance and scalability.
- HPE GreenLake: A hybrid cloud solution providing on-demand computing resources.
- HPE SimpliVity: An integrated platform that simplifies virtual server management.
Companies like Viria have embraced HPE solutions to provide efficient virtualization services for businesses.
Conclusion
Server virtualization in cloud computing is transforming IT infrastructure, offering flexibility, cost savings, and improved efficiency. Whether for web hosting, enterprise IT, or cloud computing, server virtualization in cloud computing is a crucial technology for modern businesses. Companies like Viria continue to innovate, ensuring organizations can maximize their IT resources securely and efficiently.For businesses looking to leverage server virtualization in cloud computing, understanding its benefits and challenges is essential.
Server virtualization in cloud computing revolutionizes IT by enabling multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical machine. This technology enhances resource utilization, reduces costs, and improves scalability. Businesses benefit from increased efficiency, faster deployments, and improved disaster recovery. With virtualization, organizations can optimize their IT infrastructure while maintaining flexibility. Companies like Viria are leading the way in providing cutting-edge virtualization solutions to help businesses maximize their computing power efficiently and securely.
Read also Cloud Computing Trends In Coimbatore




